Jan 23, 2026
WCO-IOF-ESCEO
Abstract
OSTEO
Clinical Performance of an AI-Based Opportunistic Osteoporosis Screening Software Using Chest Radiographs
Jinho Jung 1,2, Jin-Ri Kim3*
1 Promedius Inc., Seoul, Republic of Korea
² Evidence-Based and Clinical Research Laboratory, College of Pharmacy, Chung-Ang FUniversity, Seoul, Republic of Korea
³ Department of Family Medicine, H PLUS Yangji Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea
PURPOSE: To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of an artificial intelligence (AI)–based opportunistic osteoporosis screening software, Osteo Signal (PROS CXR-06), using posteroanterior chest radiographs, with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) as the reference standard, in adults aged 50 years and older.
METHODS: This retrospective, single-arm clinical study analyzed paired posteroanterior chest X-ray and DXA data from adults aged 50 years and older. All eligible chest radiographs were analyzed centrally using a locked version of the Osteo Signal AI algorithm. The AI output was compared with DXA-derived bone mineral density T-scores. Diagnostic performance was assessed using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) as the primary endpoint, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) as secondary endpoints. Osteoporosis was defined as a DXA T-score ≤ −2.5. Statistical analyses were conducted on the analysis set.
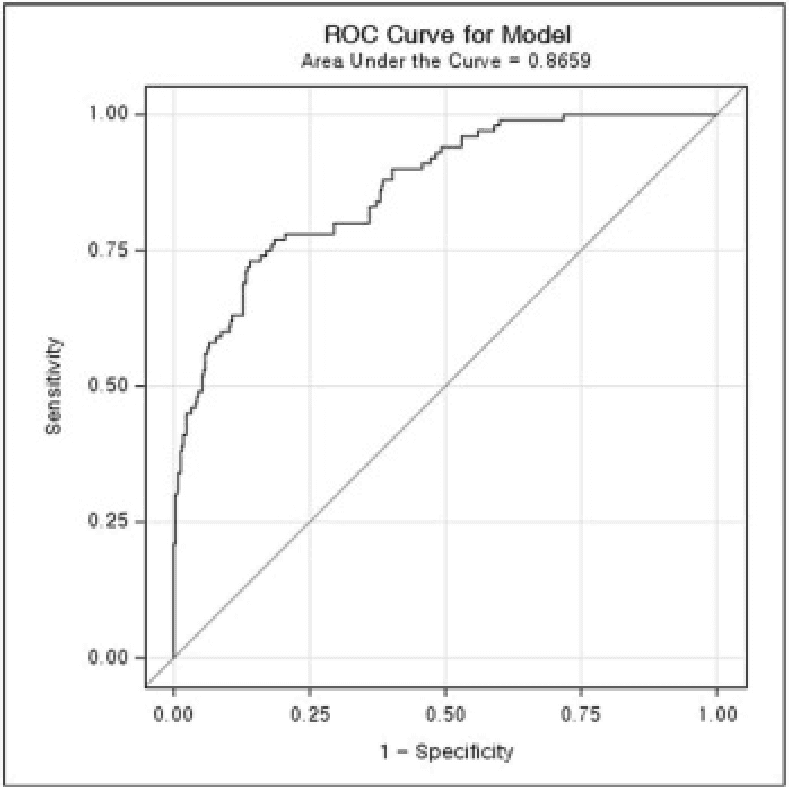
RESULTS: A total of 500 subjects were included. Osteo Signal met the predefined primary performance criterion, with the lower bound of the 95% confidence interval for AUC exceeding the threshold. The observed AUC was 0.866 (95% CI: 0.827–0.905) for detecting DXA-defined osteoporosis. Secondary performance measures showed a sensitivity of 77.0%, a specificity of 80.3%, a PPV of 49.4%, and an NPV of 93.3%. These findings demonstrated consistent screening performance in the study population.
CONCLUSION: Osteo Signal demonstrated validated screening performance for identifying individuals with osteoporosis using routine chest radiographs, without additional imaging or radiation exposure. These results confirm the clinical validity of AI-based opportunistic osteoporosis screening as a diagnostic support tool in clinical workflows.
LIMITATIONS: This study was retrospective, single-arm, and conducted at a single clinical center. Clinical outcomes, fracture incidence, or treatment initiation were not evaluated. Further multicenter prospective studies are required to assess real-world clinical impact.
FUNDING FOR THIS STUDY: This regulatory clinical study was funded by Promedius Inc., with independent data analysis and interpretation.
[Table 1] Baseline demographic characteristics (Full Analysis Set) Category Disease group
Total
N=500 p-value
Sex
N=100
Non-disease group N=400
n 100 400 500
Male 12(12.0) 106(26.5) 118(23.6) 0.002e Femal 88(88.0) 294(73.5) 382(76.4)
Age
n 100 400 500 Mean±SD 67.8±8.5 62.2±7.9 63.3±8.4 <.001b Median 69.0 61.0 62.0 Min, Max 51.0, 83.0 50.0, 83.0 50.0, 83.0
[Figure 1] Participant flow
[Figure 2] Area under the ROC curve (AUC) for osteoporosis screening (Full Analysis Set)